This plugin ensures audit logging is enabled for Redshift clusters for security and troubleshooting purposes.
Risk Level: LOW
Description:
This plugin ensures audit logging is enabled for Redshift clusters for security and troubleshooting purposes. Redshift clusters should be configured to enable audit logging to log cluster usage information.
Recommended Action: Modify Redshift clusters to enable audit logging
About the Service :
Amazon Redshift is a cloud-based, fully managed petabyte-scale data warehousing service. This allows you to gain fresh insights for your company and customers by analyzing your data. The first step in creating a data warehouse is to set up an Amazon Redshift cluster, which is a collection of machines. You can upload your data set and then run data analysis queries after you've provisioned your cluster. Regardless of the size of the data set, Amazon Redshift provides quick query performance using the same SQL-based tools and business intelligence apps you're already using.
Impact:
If the Redshift Cluster Audit Logging feature is disabled we would face security and compliance issues since we won’t be able to record database usage information such as queries performed and connection attempts. The Audit Logging feature also helps in troubleshooting errors.
Steps to reproduce :
- Sign in to your AWS management console.
- Navigate to Redshift dashboard at: https://console.aws.amazon.com/redshift/

- Select “ Clusters ” under “ Redshift Dashboard ”.
- Click and select the cluster you want to examine.
- Visit the “ Properties ” panel and check out the status of “ Audit Logging ”.
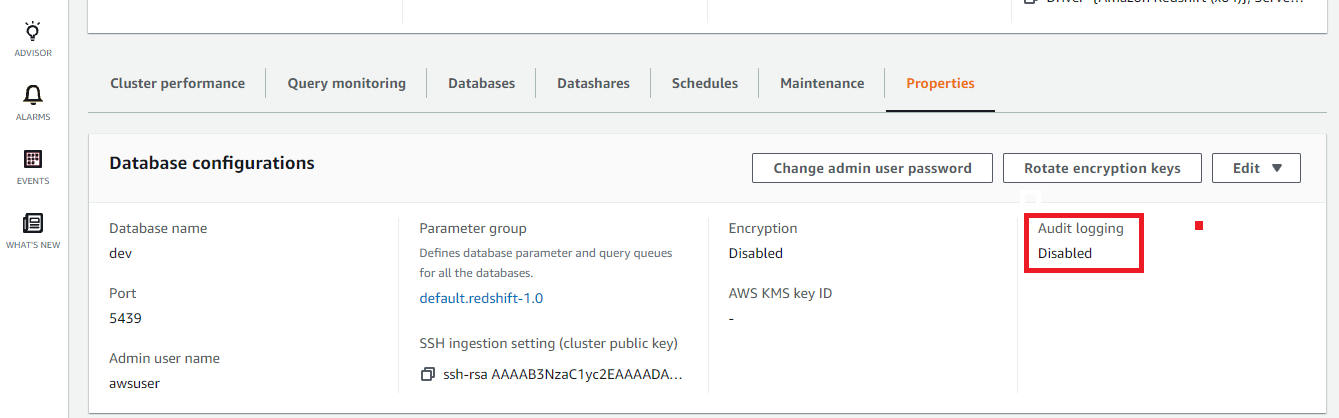
- Repeat steps 4 and 5 to verify the feature status for other Redshift clusters available in the current region as well as in different regions.
Steps for remediation :
- Sign in to your AWS management console.
- Navigate to Redshift dashboard at: https://console.aws.amazon.com/redshift/

- Select “ Clusters ” under “ Redshift Dashboard ”.
- Click and select the cluster you want to examine.

- Visit the “ Properties ” panel, click on the “ Edit ” dropdown, and select “ Edit Audit Logging ”.
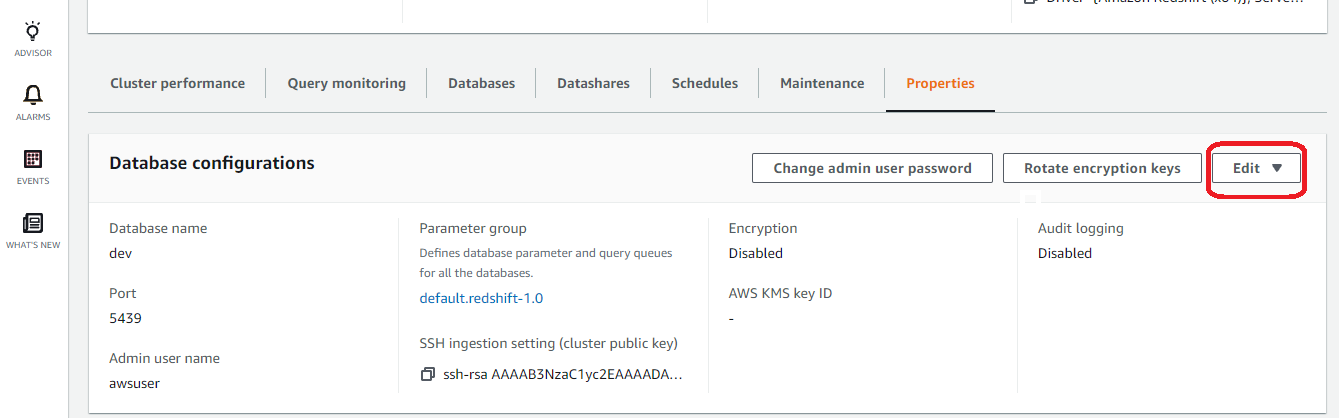
- In the “ Edit Audit Logging ” dialog box, perform the following actions:
- Select Enable under Configure audit logging.
- Choose one of the following options for S3 Bucket based on your preferences:
- To store the log files in an existing S3 bucket, select Use Existing bucket and select the bucket's name from the Bucket name dropdown list. (Optional) In the S3 Key Prefix box, you can give the log file names a unique prefix.
- Create a new S3 bucket for log file storage by selecting Create New Bucket and entering a name in the Bucket Name box. (Optional) You can give a unique prefix for the log file names generated by Redshift in the S3 Key Prefix box.
- Click Save to enable the Audit Logging feature for the selected Redshift Cluster.
- Repeat steps no. 4 - 6 to enable audit logging for other Redshift clusters provisione to the current region as well as for other regions.
References:
