Risk Level: Low
Description
The plugin checks whether or not the expiration time is set for secrets in the Azure key vault to ensure that the secrets are changing after a certain time period. This restricts expired secrets from being reused for sensitive data storage.
About the Service
Key Vaults: Azure provides a facility to store and manage sensitive data such as certificates, user ids and passwords through key vaults service. The keys are embedded in the URL which reduces the accidental or intentional exposure of the keys.
Impact
Setting up an expiration period for the keys ensures that the secret is being renewed after a certain time period and is not being used to store any sensitive information after the expiry period is met.
Steps to Reproduce
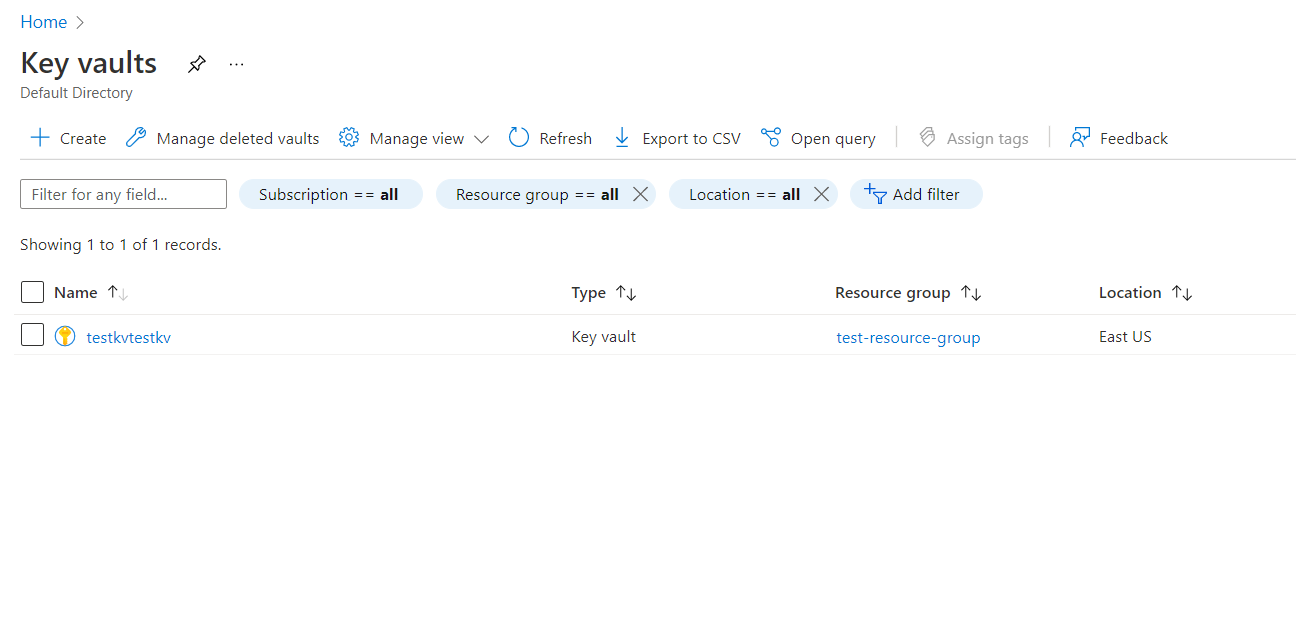
- Log in to the Azure portal.
- Click on Key vaults under Services or type “Key vaults” in the search box.
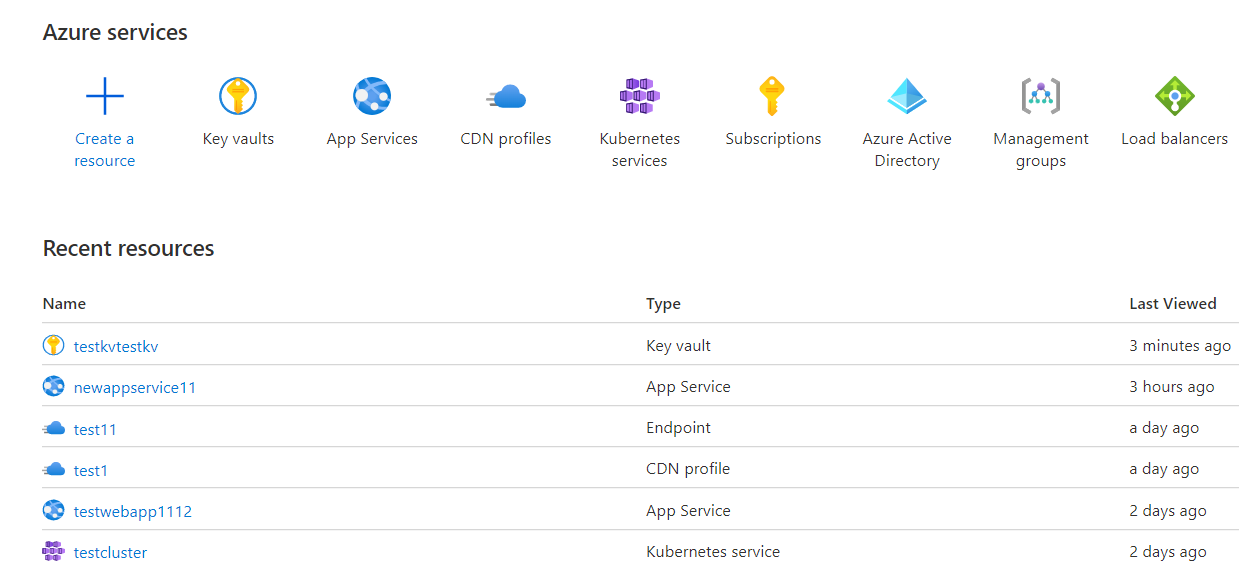
- Select a subscription to examine the issue.
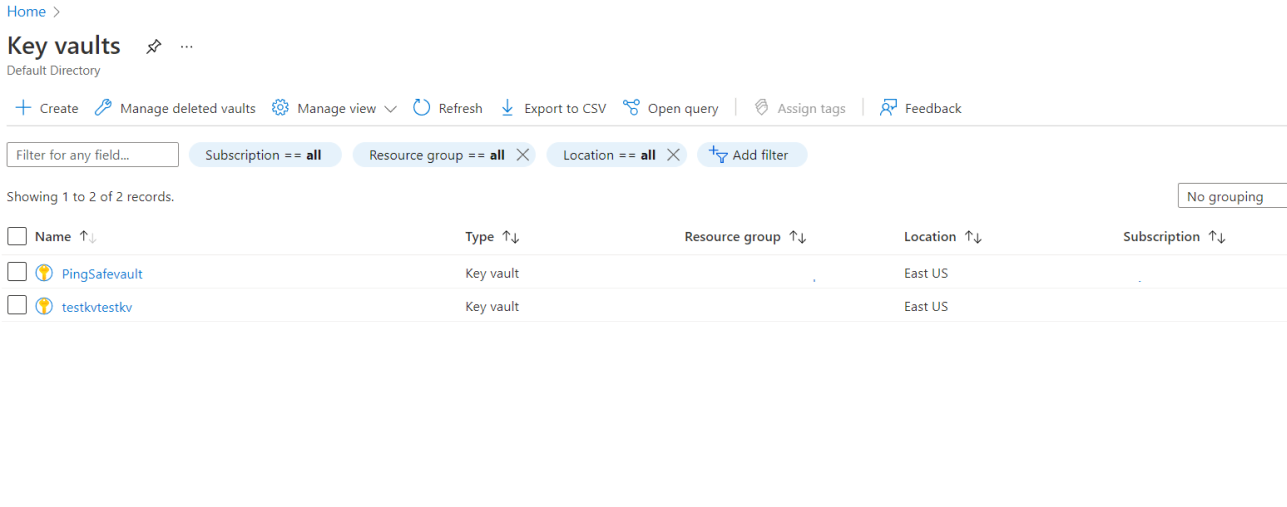
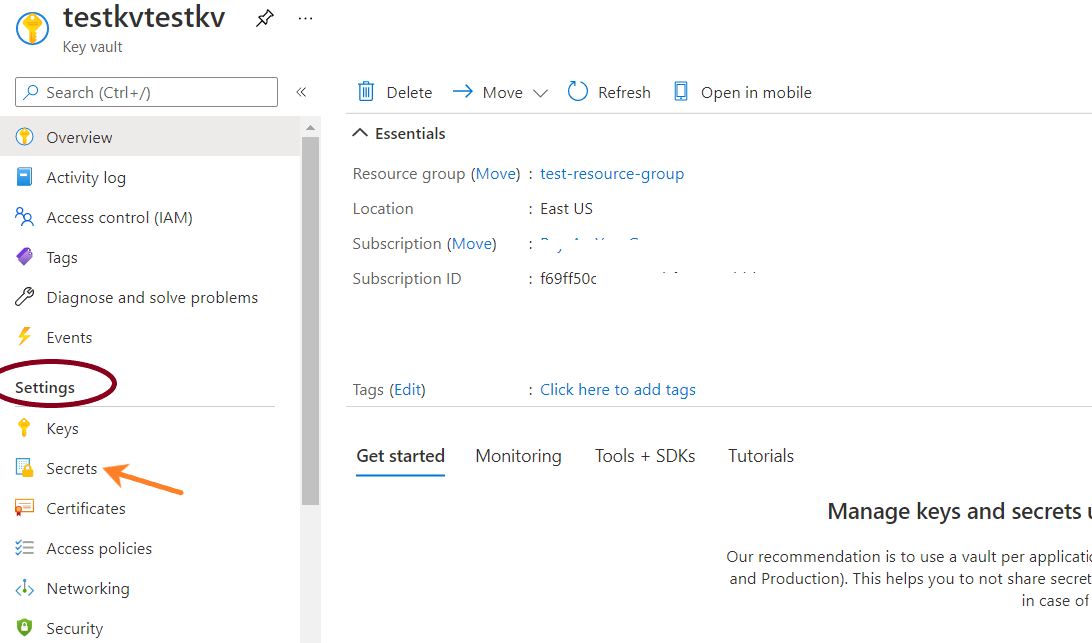
- From the navigation bar, go to Secrets under Settings.
- On the overview board, for the provided list of Secrets, if the Expiration date column is set to blank for any of the keys, visit the Steps to Remediation section.
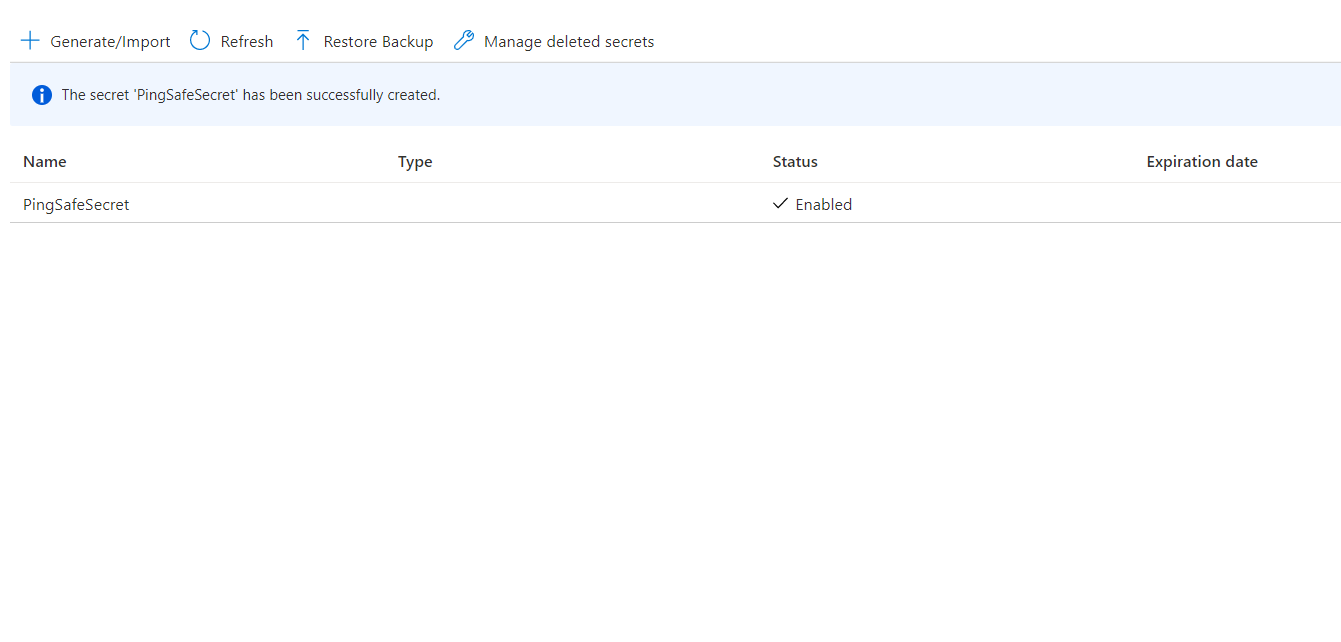
- Repeat for other secrets as well.
Steps for Remediation
- Log in to the Azure portal.
- Click on Key vaults under Services or type “Key vaults” in the search box.

- Select a subscription to examine the issue.
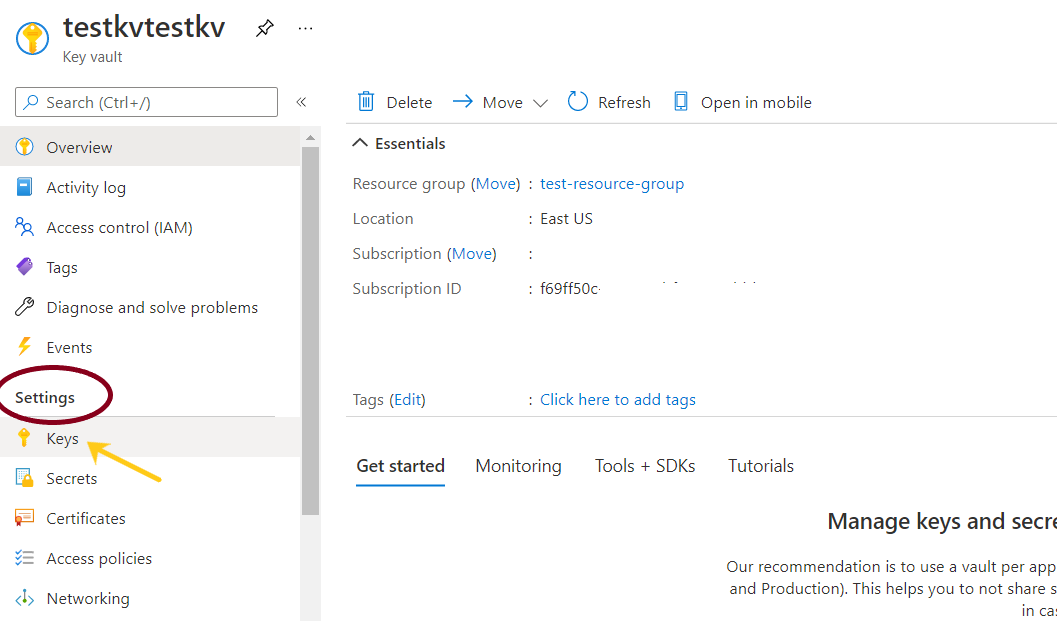
- From the navigation bar, go to keys under Settings.
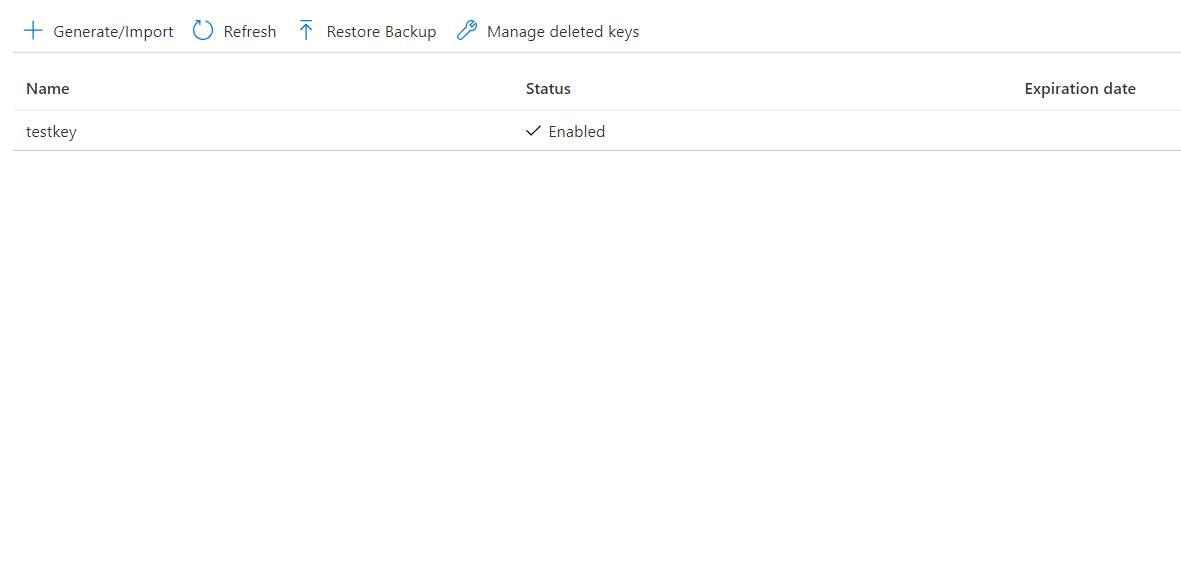
- Select the encrypted secret to enable the expiration and set the expiry date.
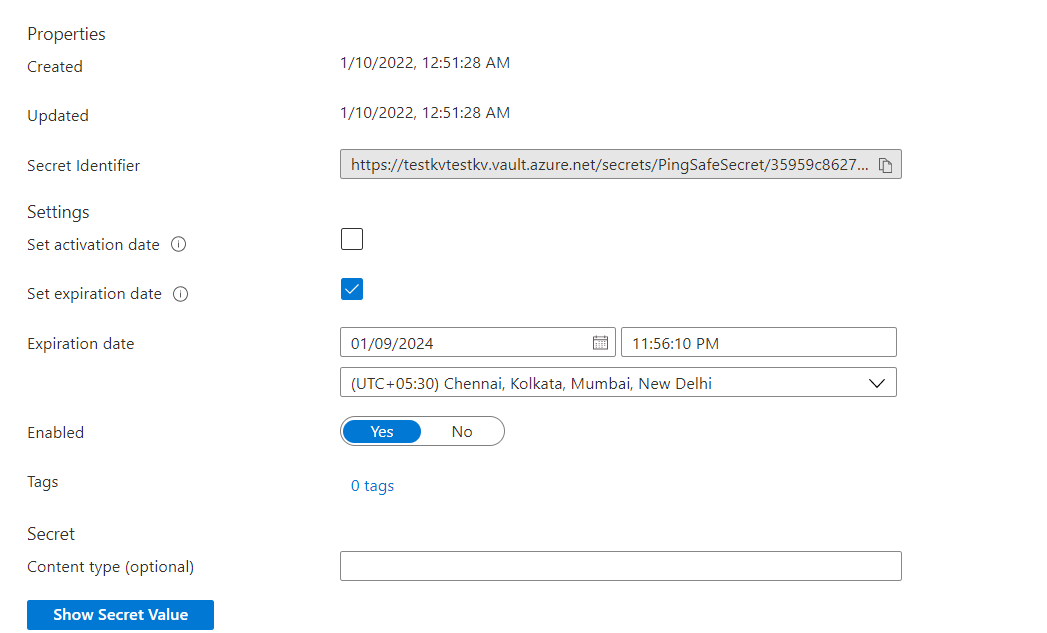
- Click on the check box given in front of Set Expiration date, mention the expiry date and time and set the time zone as required in front of the Expiration date. Click on Save.
- Repeat for other secrets as well.
Please feel free to reach out to support@pingsafe.ai with any questions that you may have.
Thanks
PingSafe Support
